Spring IOC
Spring IOC 练习的代码地址:
https://github.com/hzebin/SpringIOC
=====================================
Spring IOC的底层原理:工厂模式 + 反射 + 配置文件 【为了减少程序之间的耦合性】
IOC (Inverse of Control)控制反转,将原本在程序中手动创建的对象(例如UserService)的控制权,交由Spring框架管理。
DI(Dependency Injection)依赖注入,就是在Spring创建这个对象的过程中,将这个对象所依赖的属性注入进去。
使用Spring IOC需要导入的jar包
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
spring-beans
spring-context
spring-core
spring-expression
commons-logging
log4j
junit
|
Spring的Bean管理(XML方式)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
</beans>
|
Bean的实例化有三种方式:
- 采用无参数的构造方法方式
- 静态工厂的实例化方式
- 实例工厂实例化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
<bean id="bean1" class="cn.hzebin.ioc.demo2.Bean1"></bean>
<bean id="bean2" class="cn.hzebin.ioc.demo2.Bean2Factory" factory-method="createBean2"></bean>
<bean id="bean3Factory" class="cn.hzebin.ioc.demo2.Bean3Factory"></bean>
<bean id="bean3" factory-bean="bean3Factory" factory-method="createBean3"></bean>
|
Bean配置里的属性:
id和name:
id和name效果是一样的。一般情况下装配一个Bean时,通过指定一个id属性作为Bean的名称。
id属性在IOC容器中必须是唯一的。
如果Bean的名称中含有特殊字符(例如name=”/studentService”),就要改为使用name属性(id不能含有特殊字符)。
class:
class用于设置一个类的完全路径名称,主要的作用是给IOC容器生成类的实例。
Bean的作用域属性scope:
| 类别 |
说明 |
| singleton(默认情况下是单例) |
在SpringIOC容器中仅存在一个Bean实例,Bean以单实例的方式存在 |
| prototype(多例) |
每次调用getBean()时都会返回一个新的实例 |
| request |
每次HTTP请求都会创建一个新的Bean,该作用域只适合于WebApplicationContext环境 |
| session |
同一个HTTP Session共享一个Bean,不同的HTTP Session使用不同的Bean。该作用域只适合于WebApplicationContext环境 |
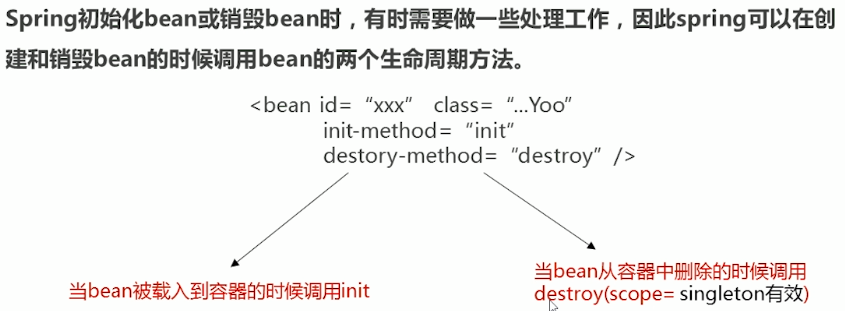
init-method和destory-method属性
20190108A.png
Tip:如果是多例的话,程序不知道销毁谁
Spring的属性注入–构造方法注入
1
2
3
4
5
|
<bean id="user" class="cn.hzebin.ioc.demo4.User">
<constructor-arg name="name" value="黄泽彬"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="age" value="22"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
|
Spring的属性注入–set方法注入
- 使用set方法注入,在Spring配置文件中,通过设置注入的属性
1
2
3
4
5
6
| <bean id="person" class="cn.hzebin.ioc.demo4.Person">
<property name="name" value="熊君"></property>
<property name="age" value="22"></property>
<property name="cat" ref="cat"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="cat" class="cn.hzebin.ioc.demo4.Cat"></bean>
|
Spring的属性注入–p名称空间
- 为了简化XML文件配置,Spring2.5开始引入一个新的p名称空间
- p:<属性名> = “xxx” 引入常量值
- p:<属性名>-ref = “xxx” 引入其他Bean对象
1
2
3
4
5
| 需要在applicationContext.xml头部添加:
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
<bean id="cat" class="cn.hzebin.ioc.demo4.Cat" p:name="小猫"></bean>
<bean id="person" class="cn.hzebin.ioc.demo4.Person" p:name="胡文瀚" p:age="23" p:cat-ref="cat"></bean>
|
Spring的属性注入–SpEL注入(Spring expresssion language)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
<bean id="category" class="cn.hzebin.ioc.demo4.Category">
<property name="name" value="#{'服装'}"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="productInfo" class="cn.hzebin.ioc.demo4.ProductInfo"></bean>
<bean id="product" class="cn.hzebin.ioc.demo4.Product">
<property name="name" value="#{'裤子'}"></property>
<property name="price" value="#{productInfo.calculatePrice()}"></property>
<property name="category" value="#{category}"></property>
</bean>
|
Spring的复杂类型的属性注入
类型包括:数组、List集合、Set集合、Map集合、Properties
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
|
<bean id="collectionBean" class="cn.hzebin.ioc.demo5.CollectionBean">
<property name="arrs">
<list>
<value>aaa</value>
<value>bbb</value>
<value>ccc</value>
</list>
</property>
<property name="list">
<list>
<value>111</value>
<value>222</value>
<value>333</value>
</list>
</property>
<property name="set">
<set>
<value>ddd</value>
<value>eee</value>
<value>fff</value>
</set>
</property>
<property name="map">
<map>
<entry key="aaa" value="111"></entry>
<entry key="bbb" value="222"></entry>
<entry key="ccc" value="333"></entry>
</map>
</property>
<property name="properties">
<props>
<prop key="username">root</prop>
<prop key="password">root1234</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
|
使用注解定义Bean
使用Spring注解的使用需要引入的jar包:spring-aop
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="cn.hzebin"></context:component-scan>
</beans>
|
| 注解 |
说明 |
| @Component |
描述Spring框架中的Bean(相当于id) |
| 上面这个注解与下面的注解等价,推荐使用下面的注解 |
|
| @Repository |
用于对Dao实现类进行标注 |
| @Service |
用于对Service实现类进行标注 |
| @Controller |
用于对Controller实现类进行标注 |
| 注解 |
说明 |
| @Value(“”) |
给属性添加值的注解 |
| 注解 |
说明 |
| @Autowired |
属性注入,默认按类型注入(id名不相同也行),也可以按id名称注入 |
| 注解 |
说明 |
| @Autowired @Qualifier(“userDao”) |
注入的类型和id名称都要相同 |
| 上面的注解与下面的注解等价 |
|
| @Resource(name = “”) |
|
| 注解 |
说明 |
| @PostConstruct |
初始化,当Bean被载入导容器的时候调用该方法,与init-method作用相同 |
| @PreDestroy |
销毁,当Bean从容器中删除的时候调用该方法(单例才有效,与destory-method作用相同) |
| @Scope(“”) |
Bean的作用域 |
XML配置和注解各有优缺点,可以将XML配置与注解配置混合使用
XML配置的优点:结构清晰、易于理解
注解配置的优点:开发便捷、属性注入方便
XML与注解整合开发
【使用XML来管理类,使用注解来进行属性注入】
使用步骤:
- 引入context命名空间
- 在配置文件中添加context:annotattion-config标签 【意思:开启属性注入注解,禁止类注解】